Data entry is a tedious process that requires a lot of attention to the most minute details. It is prone to errors that can affect the results of data analysis later down the line.
Fortunately with modern technology and as information management evolves, automating this process has been the new trend for professionals and businesses alike.
In this blog, we’ll talk about the differences between manual and automated data entry. Including its pros and cons, as well as what cases it is appropriate to use.
Level up your accounting game with AI – Download our eBook today
Key Takeaways:
- Manual data entry is prone to errors and less efficient, suitable for small, complex tasks requiring human judgment, but has higher long-term costs.
- Automated data entry boasts high accuracy, efficiency, and scalability, ideal for large volumes and repetitive tasks, with initial setup costs but lower operational expenses.
- Flexibility is a strength of manual data entry, adapting easily to various data formats, while automated systems need updates for new formats but are improving with AI.
- Manual entry requires significant human effort and quality control, whereas automated systems ensure consistency and integrate well into digital workflows, reducing error rates and costs.
- Choosing between manual and automated data entry depends on the data volume, complexity, need for speed, and cost efficiency, with automation favored for large-scale, repetitive tasks.
Comparing Manual and Automated Data Entry
There are major differences between manual and automated data entry, but automation certainly stands out in a fast-paced environment.
Here are some of the notable differences between automated data entry and manual data entry:
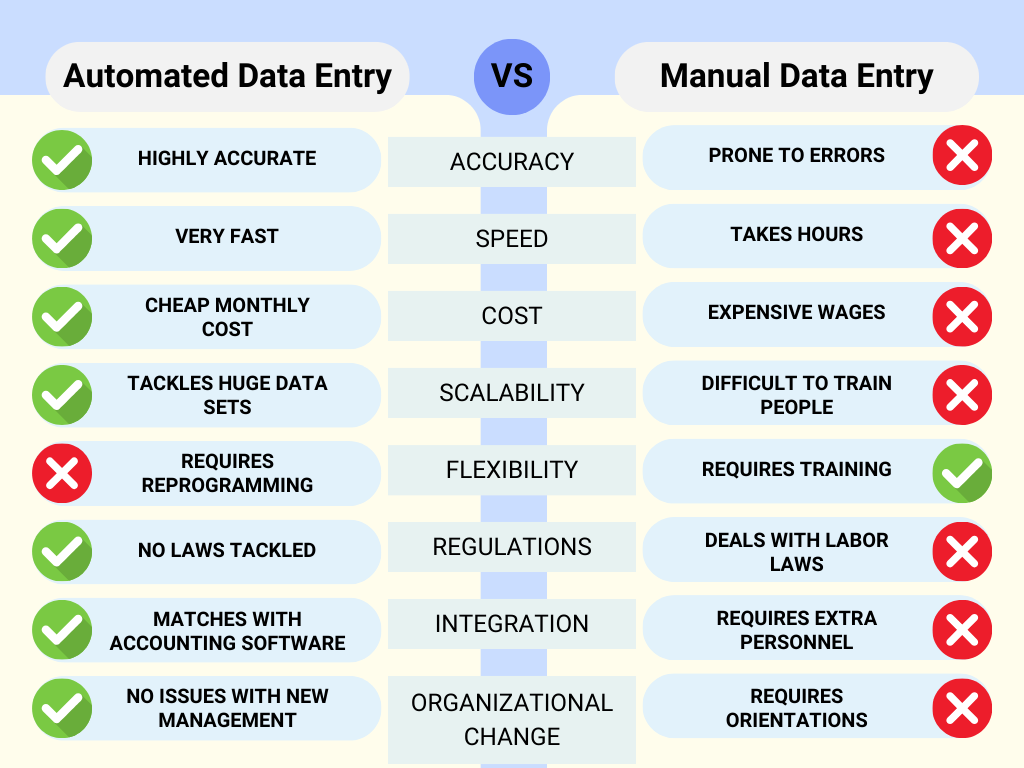
| Manual Data Entry | Automated Data Entry | |
| Accuracy | Prone to human errors and dependent on the condition of the person inputting | High accuracy due to reduced human errors; depends on software quality. |
| Speed & Efficiency | Slow and less efficient, limited by human capacity and need for breaks. | Fast and efficient, capable of processing large volumes of data quickly |
| Cost Differences | Lower initial costs but higher long-term expenses due to labor. | Higher initial investment but lower operational costs over time. |
| Scalability | Difficult to scale up quickly; requires more staff and resources. | Easily scalable, handling increased data volumes without significant resource increases. |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to changes in data formats and requirements. | Less flexible; requires updates or reprogramming to adapt to changes. |
| Regulations | Compliance is dependent on training, with the potential for human error. | Can be programmed for consistent compliance, reducing the risk of error. |
| Workflow Integration | May require extra steps for integration into digital workflows. | Easily integrates into digital workflows, enhancing overall process efficiency. |
| Organizational Change | Adaptable with minimal structural changes; primarily requires training. | May require significant changes, including software updates. |
Accuracy
Manual Data Entry: Manual data entry’s accuracy is heavily dependent on the personnel performing the task. The likelihood of human error increases with fatigue, lack of attention, or misunderstanding of instructions, which can compromise data quality. it requires a rigorous quality control process to catch and correct errors, which can be time-consuming and costly.
Error rates of manual data entry can run up to 4% in some fields. While it varies depending on the context like industry and complexity. These error risks can affect the entire efficiency of the workflow.
Automated Data Entry: Automated data entry systems have superior accuracy levels by minimizing the margin for human error. These systems depend on the initial setup and the algorithms’ quality, which can accurately process vast amounts of data consistently.
OCR accuracy in automated systems is top-notch with a record of 99.5% in specific niche uses like converting bank statements or invoices.
Speed & Efficiency
Manual Data Entry: The process of manually typing data is slow and inefficient, particularly as data volumes increase. The speed of data entry is limited by human capabilities, with individuals needing breaks and susceptible to fluctuations in performance. In high-paced environments, these limitations can be blockers, delaying data availability for decision-making processes.
Automated Data Entry: Automating data entry speeds up processing and improves efficiency, allowing systems to work non-stop and handle tasks faster than humans. These systems and algorithms can process and analyze large amounts of data in a few minutes.
Cost
Manual Data Entry: Initially, manual data entry seems cheaper, but long-term costs like labor, training, and error correction add up. As data and organizational needs grow, these costs escalate, making manual entry expensive over time.
Statistics show that the median data entry personnel’s annual salary is around $36,190. Making it a huge sum for the long term. (Data entry statistics)
Automated Data Entry: Shifting to automated data entry involves significant initial costs for technology, customization, and training. However, the long-term benefits include reduced labor and error costs and improved efficiency. As the system scales, the cost per data unit processed drops. And it’s better than outsourced data entry or outsourced bookkeeping.
Scalability
Manual Data Entry: Scaling manual data entry is challenging. More data means hiring more staff, leading to slow and costly expansion. This increases management complexity and quality control issues. Since data volume directly impacts staff needs, manual data entry becomes less viable for businesses facing rapidly growing or fluctuating data demands.
Automated Data Entry: Automated data entry excels in scalability. It can manage more data without needing much more resources or costs. Scaling up usually just needs small tweaks, helping businesses quickly adapt to more data.
Automation typically uses OCR data entry software as it can process multiple repetitive information in one go. To put into example, OCR bank statement converters can process thousands of bank statements in hours but only for this niche.
Flexibility
Manual Data Entry: Manual data entry’s strength is its adaptability. Humans can quickly adjust to different data formats or structures with little guidance, ideal for tasks with varying data types and sources. This flexibility is useful when dealing with non-standard data or when judgment is needed in data interpretation.
Automated Data Entry: Automated systems struggle with flexibility, requiring updates for new data formats, which can be slow and costly. However, advancements in AI and machine learning are improving their adaptability to different data types and sources. This progress suggests future automated data entry will be more flexible, reducing the need for manual adjustments.
This is one of OCR’s limitations as most of these systems are tied to specific niches. While there are general-purpose OCR systems out there, they have issues in formatting and require intensive customization to give a formatted result.
Regulations
Manual Data Entry: Hiring people means you have to follow labor rules, like handling tax forms and giving benefits. Sometimes, the rules can be tricky, which might affect how well the company does. Do you want to know how to learn data entry? Visit our article to learn more.
Automated Data Entry: Using software to enter data usually doesn’t have these rule issues. The main problems come when people lose their jobs because of the switch to tech, and there are also concerns about cybersecurity.
Workflow Integration
Manual Data Entry: Creating standardized workflows is challenging with manual data entry. Since everyone works differently and can make mistakes, it’s hard to ensure they always follow set standards. This variability can disrupt smooth workflow processes.
Automated Data Entry: Automated data entry software excels at fitting into established workflows. It consistently delivers data in standardized formats, providing predictable and easily integrated outputs. This reliability enhances workflow efficiency and accuracy

Organizational Change
Manual Data Entry: When employees leave, manual data entry faces challenges. Training new staff takes time and often leads to more mistakes, affecting productivity and accuracy. Adapting to these changes can slow down processes significantly.
Automated Data Entry: Automated data entry systems simplify transitions when employees leave. Training new staff is generally less complex, as the system provides consistency and stability, minimizing disruptions and maintaining workflow efficiency.
Summary of Manual vs Automated Data Entry
Manual data entry offers flexibility and adaptability, ideal for varied data types but slower and error-prone. Automated data entry excels in efficiency, speed, and scalability, with improving adaptability through technology. The choice depends on an organization’s specific needs, data volume, and operational dynamics.
What is Manual Data Entry?
Manual data entry involves physically inputting data into a system or database by human operators. This process can include typing information from paper documents, entering data from physical forms, or manually updating records.
It requires significant human effort and is highly reliant on the accuracy and speed of the data entry personnel.
What is Automated Data Entry?
Automated data entry uses software, algorithms, and sometimes hardware to input data into systems without direct human intervention. Opposite to manual data entry, this method delivers fast results in entering data.
This can involve scanning documents and using optical character recognition (OCR) to convert them into digital formats, importing data from one system to another, or using web scraping tools to gather information automatically.
In specific niches as mentioned earlier, automated data entry uses OCR technology, especially in finance and accounting. Accounting professionals highly automated software to provide accurate results as it can be a problem if there are inaccuracies. It is also a fast way to process many numbers at the same time.
To learn more about how to automate data entry in accounting here are some articles:
- How to Convert Bank Statements to Excel, CSV, or QBO
- Import Bank Transactions into Quickbooks Online
- Import Bank Transactions into Quickbooks Desktop
When to Choose Manual Data Entry
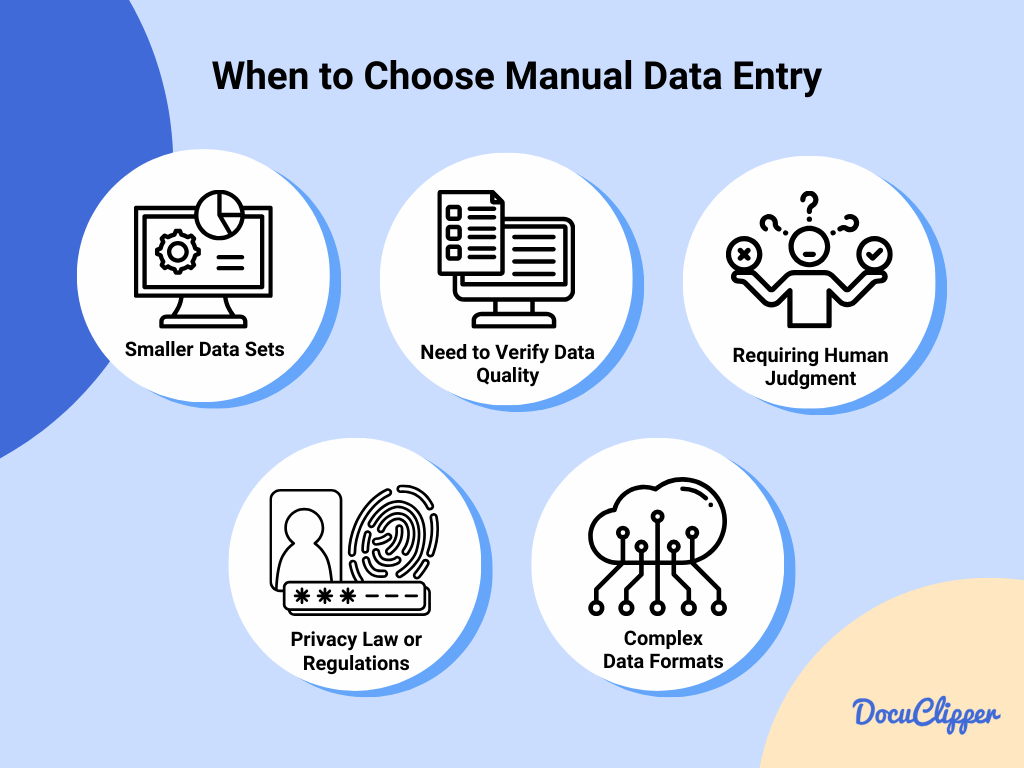
Choosing manual data entry is advantageous in specific scenarios where human flexibility, understanding, and judgment are paramount. This approach suits various situations, including:
- Smaller Data Sets: For projects with limited amounts of data, manual entry can be more cost-effective.
- Need to Verify Data Quality: Situations requiring high accuracy and the opportunity for human oversight to catch errors.
- Data Requiring Human Judgment: Complex decisions that require understanding context, nuances, or unstructured data interpretation.
- Privacy or Regulations Law: When data handling must adhere strictly to privacy laws or regulations, requiring careful, personalized management.
- Complex or Non-Standard Data Formats: Data that automated systems cannot easily interpret or require specialized knowledge to process.
When to Choose Automated Data Entry
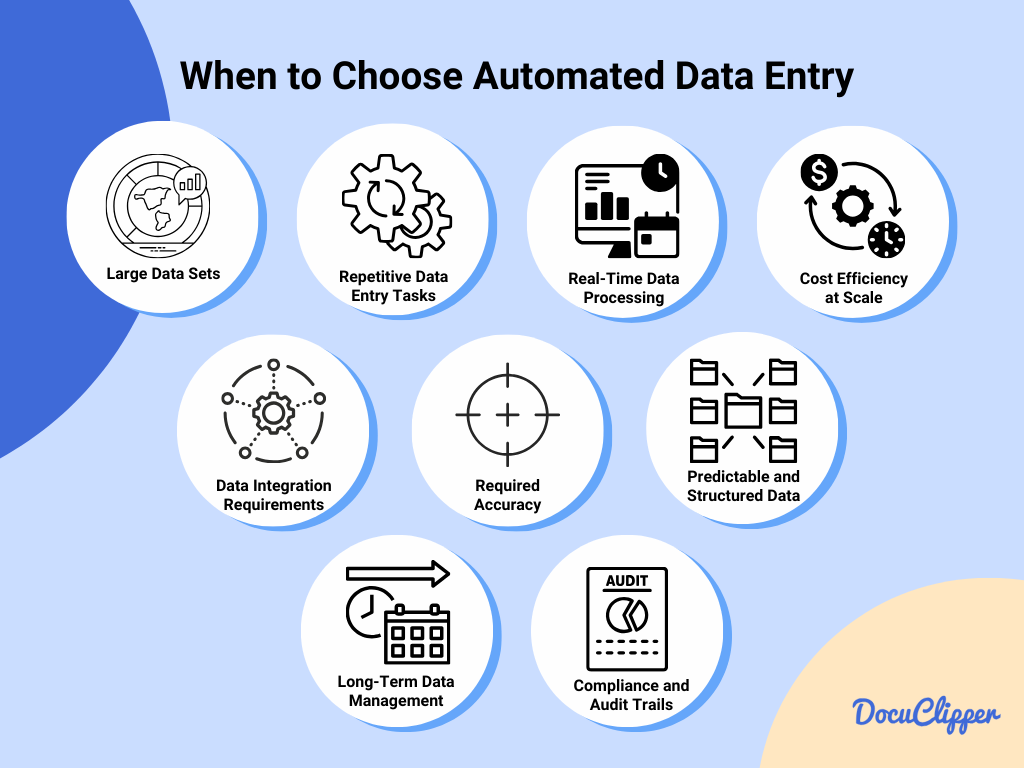
Automated data entry is the go-to solution for handling large volumes of data with efficiency, accuracy, and speed.
It’s particularly beneficial in situation like:
- Large Volume Data Processing: For handling vast amounts of data efficiently.
- Repetitive Data Entry Tasks: Automating routine tasks reduces errors and frees up human resources.
- Real-Time Data Processing Needs: When data needs to be processed immediately for timely insights or actions.
- Cost Efficiency at Scale: Reducing the per-unit cost of data processing in large-scale operations.
- Data Integration Requirements: Seamlessly merging data from multiple sources into a unified system.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Consistency: Minimizing human error in data entry and ensuring uniform data handling.
- Predictable and Structured Data: Data that follows a consistent format, ideal for automation.
- Long-Term Data Management Strategy: Building a scalable, efficient data management framework.
- Compliance and Audit Trails: Automated systems can ensure adherence to regulations and easily track data handling processes.
Implementing Automated Data Entry Systems
Incorporating automated data entry systems into an organization requires careful planning and consideration of several factors to ensure success and efficiency:
- Types of Automated Entry Systems: Includes OCR, data capture solutions, and software integration platforms.
- Integration Considerations: Ensuring the new system works seamlessly with existing databases and software.
- Error Checking Protocols: Establishing automated checks to identify and correct data inaccuracies, enhancing reliability.
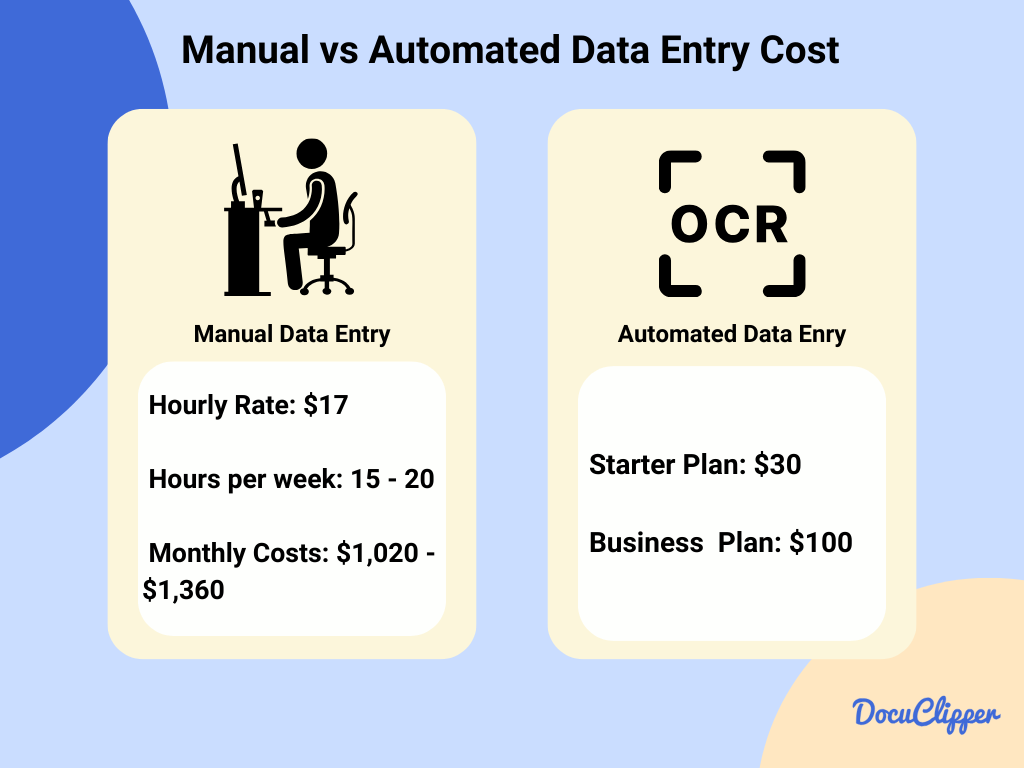
Cost of Manual & Automated Data Entry
The cost of using manual or automated ways to enter data changes based on the type of job. Paying someone to enter data by hand costs about $17 an hour. This might seem cheap at first, but over time, it adds up because you keep needing people to do this work.
Using automated data entry can significantly cover more work per hour as some people who employ automation can save up to 26 hours of work in a week.
But, the software that makes it work starts at just $20, and if a business needs more features, it could pay around $100.
Automated data entry especially automated bookkeeping can save money later on by reducing the need for a lot of manual work, speeding up data entry, and making fewer mistakes.
Conclusion
Choosing between automated and manual data entry depends on your specific needs, budget, and the nature of the data being handled.
Automated systems offer long-term savings, efficiency, and accuracy but require an initial investment. Manual data entry provides flexibility and is easier to implement for small or complex tasks but can be costly and less efficient over time.
FAQs about Automated vs Manual Data Entry
Here are some of the frequently asked questions about automated and manual data entry systems:
Why is data entry not automated?
Data entry might not be automated due to the initial cost of setting up automated systems, the complexity of the data, or specific requirements for human judgment and flexibility in handling non-standard data formats or sensitive information.
Can you automate data entry work?
Yes, data entry work can be automated, especially for repetitive, large-volume tasks or when dealing with structured data. Automation can significantly reduce manual effort and increase accuracy.
Can you automate data entry in Excel?
Yes, you can automate data entry in Excel using various tools and features like macros, form controls, and Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) scripting to streamline repetitive tasks and data processing.
Is it possible to automate the data entry job?
Many data entry jobs can be automated, particularly those involving repetitive tasks and standard data processing. However, jobs requiring complex decision-making or handling of non-standard data may still need manual intervention.
How can I improve my manual data entry?
Improving manual data entry involves training staff for higher accuracy and speed, implementing double-entry verification to reduce errors, and using software tools to assist in data validation and entry tasks.
Is data entry stressful?
Data entry can be stressful due to the monotony of repetitive tasks, the pressure to maintain high accuracy and speed, and the potential for long periods of sedentary work, which can affect physical and mental health.
What is an example of automated data processing?
An example of automated data processing is the use of OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology to scan paper documents and convert them into digital text, which can then be processed, stored, or analyzed by software without manual typing.